|
Final Exam---QUIZ 10
|
|
1 The source of all magnetism is
|
|
a. tiny pieces of iron
|
|
b. the force of gravity
|
|
c. electric charge in motion
|
|
d. nota
|
|
2 True of False. A current in a conducting wire does produce a
magnetic field.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
3 A conducting long straight wire
loop lies vertically in the plane of the page. A current flows upward through
the wire. What is the direction of the magnetic field directly to the right
of the wire? (It would help if you sketched the
vertical straight line and drew an arrow pointing up on the line representing
the current. Hint: Use the right hand rule for long straight
wires by pointing your right thumb upward in
the direction of the current. Your right fingers will
point in the direction of the magnetic field on the right of the line.)
|
|
a. in
|
|
b. out
|
|
c. nota
|
|
4 True or False. A magnetic field does not exert
a force on a charge in motion.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
5 True or
False. The magnetic force on a charge moving in a magnetic field is perpendicular to the velocity of the particle.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
6. True or False. The magnetic force on a
charge moving in a magnetic field
is perpendicular to the
magnetic field.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
7 True or
False. The magnetic force on a straight, current
carrying wire in an external magnetic field is not perpendicular to the current.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
8 True or False. The magnetic force on a
straight, current carrying wire in an external
magnetic field is not perpendicular to the magnetic field.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
9 2 long straight wires
are parallel and their currents flow in the same direction. The two wires
|
|
a. attract each other
|
|
b. repel each other
|
|
10 True or False. The geographic south pole of
the Earth coincides with the Earth's magnetic north pole.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
11. True or False. Magnetic field lines come out of the south
pole and
enter the north pole of a magnet.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
12.True or False. A length of
wire is bent into a closed loop and a magnet
near the loop is moving relative to loop. The current in the loop is
zero.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
13. True or False. A length of wire is bent
into a closed loop and a magnet within the
loop is pulled (moved) away from the loop. The current in the loop
will be zero.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
14. A circular loop of copper wire is lying flat on a
horizontal table. A bar magnet is held with its North pole downward
vertically above the center of the coil. The magnet is released from
rest and falls toward the coil. As viewed from above, as it falls, the
magnet induces
|
|
a. a counter-clockwise current in the loop
|
|
b. a clockwise current in the loop
|
|
15. According to Faraday's Law, a current flows in a
loop of wire when there is a change in
|
|
a. the electric field
intensity through the loop.
|
|
b. the magnetic field
intensity through the loop.
|
|
16. A device that transforms mechanical energy into
electrical energy is a
|
|
a. generator
|
|
b. motor
|
|
c. transformer
|
|
d. nota
|
|
17. A device that transforms electrical energy
into mechanical energy is a
|
|
a. generator
|
|
b. motor
|
|
c. transformer
|
|
d. nota
|
|
18. A big Neon sign requires about 12,000 volts (output
voltage) to operate. The "step up"
transformer circuit uses a 120-Volt (input voltage) source. What
is the ratio of primary to secondary turns on the transformer?
|
|
a. 1/100 b. 100/1 c. 200/1
d. nota
|
|
19. True or False. Most of the waves in the
electromagnetic spectrum are visible to the naked eye.
|
|
a. True
|
|
b. False
|
|
20. The main difference between ganma-ray waves and micro-waves in a vacuum is
the
|
|
a. wave speed
|
|
b. wavelength
|
|
21. Which of these waves has the
largest frequency?
|
|
a. yellow light
waves
|
|
b. infrared waves
|
|
c. X-Rays
|
|
d. ultraviolet waves
|
|
22. Which of these waves has the shortest wavelength?
|
|
a. infra-red waves
|
|
b. radio waves
|
|
c. visible yellow light
|
|
d. micro-waves
|
|
23. Which does not require a physical medium in
which to travel?
|
|
a. x-ray waves
b. sound waves
|
|
24. The natural
frequency of vibrating electrons in atoms of glass is in the
|
|
a. infrared part of the spectrum
|
|
b. visible part of the spectrum
|
|
c. microwave part of the spectrum
|
|
|
d. nota
|
|
25. The speed of light in water is
|
|
a. more than its speed in a vacuum
|
|
b. less than its speed in a vacuum
|
|
c. the same as its speed in a vacuum
|
|
26. Compared
to its speed in a vacuum, the average speed of a beam of light in glass
is
|
|
a. more
|
|
b. less
|
|
c. the same
|
|
27. The technical field of “fiber optics” is based mostly
on what principle?
|
|
(a) light polarization (b) Helium-Neon atomic collisions (c)
sound propagation in glass (d) the alignment of Mars with Venus (e) nota
|
|
28. When a light ray passes from air into water, the
light ray
|
|
(a) bends toward the normal line (b) bends away from
the normal line (c) does not change direction (d) nota
|
|
29. When a light ray passes
from glass into air, the light ray
|
|
(a) bends toward the normal line (b) bends away from
the normal line (c) does not change direction (d) nota
|
|
30. The virtual image formed by a convex mirror is
|
|
(a) equal in size and is the same distance from the mirror
as the object (b) larger and farther
away from mirror than the object (c) nota
|
|
31. The virtual image formed by a plane
mirror is
|
|
(a) equal in size and is the same distance from the mirror
as the object (b) larger and farther
away from mirror than the object (c) nota
|
|
32. Can a convex mirror form a real image?
|
|
(a) yes (b) no
|
|
33. You are driving on a dry, sunny, summer day down a hot
road with no clouds or rain in
sight. A spectacular illustration of refraction
is
|
|
(a) a mirage
(b) a rainbow (c) nota
|
|
34. Refraction mainly involves the idea that
|
|
(a) light waves of different frequencies in a medium have
different amplitudes (b) light waves
change their average speed in going from one transparent medium to another (c) nota
|
|
|
35. A double
slit arrangement causes interference fringes for yellow light. To produce
narrower–spaced slits, what type of light should be
used ?
|
|
(a) red light (b)
blue light (c) nota
|
|
36. If the path length difference between two identical
and coherent beams is two wavelengths when they arrive at the screen, they
produce a (a) dark
spot (b) light spot.
|
|
37. When the
reflected path from one surface of a thin film is one full wavelength
different in length from the reflected path from the other surface and no
phase change occurs, the result will be
(a) constructive interference (b) destructive interference
|
|
38. When the reflected path from one surface of a thin
film is one -half wavelength different in length from the reflected path from
the other surface and no phase change occurs, the result will be
(a) constructive interference (b) destructive interference
|
|
39. What
percentage of light is transmitted by two ideal Polaroids
one on top of the other with their polarization axes aligned?
(a) 0 %
(b) 100 % (c) nota
|
|
40. What
percentage of light is transmitted by two ideal Polaroids
one on top of the other with their polarization axes at right angles to each
other?
(a) 0 %
(b) 100 % (c) nota
|
|
41. Why is a gamma ray photon more energetic than an
X-ray photon?
(a) because it has a larger speed (b) because it has a larger wavelength (c)
because it has a larger frequency (d)
nota
|
|
42. Green light is emitted when electrons in a
substance make a particular energy – level transition. If blue light were
emitted instead from the same substance, the light would correspond
(a) a greater change of energy in the
atom (b) a lesser change of energy in the atom (c) nota
|
|
43. If we double the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation, what happens
to the energy of its photons?
(a) doubles (b) reduced by a factor of
one-half (c) does not change
|
|
44. Which has the greatest energy, a photon of (a) visible light (b)
infrared radiation (c) ultra-violet radiation ?
|
|
45. Fluorescent materials are noteworthy because they are excited by
ultraviolet radiation and upon de-excitation emit (a) gamma radiation (b)
visible light (c) x-rays (d) nota
|
|
46. The frequency of a violet photon is about
twice that of red light. How does the energy E of a violet photon
compare with the energy of a red photon?
|
|
a. The energy is twice the energy of a red
photon
|
|
b. The energy is one half the energy of a red photon
|
|
c. same energy
|
|
47. The photoelectric effect best illustrates the
|
|
a. wave nature of matter
|
|
b. particle nature of light
|
|
c. wave nature of light
|
|
d. nota
|
|
48. In the photoelectric effect, the higher the
frequency of the illuminating light on
the photosensitive surface, the greater the
|
|
a. number of ejected electrons
|
|
b. kinetic energy of ejected electrons
|
|
c. nota
|
|
49. Does the DeBroglie
wavelength of an electron become longer or
shorter as the momentum increases ? a. longer b. shorter c.
remains the same
|
|
50. Which of the
following is evidence of the wave nature of electrons?
(a) the photoelectric effect
(b) the interference pattern on a screen when a beam of electrons is directed through double slits.
|
|
51. One electron travels twice as fast as another.
Which has the longer wavelength? (a) faster electron (b) slower electron (c)
wavelengths are the same
|
|
52. A hydrogen
atom and a uranium atom move at the same speed. Which has the
largest wavelength?
(a) hydrogen atom (b) uranium atom (c)
nota
|
|
53. In the photo–electric effect which determines the
kinetic energy of the ejected electrons ? (a) the
brightness of the incident light (b) the frequency of the incident light (c)
nota
|
|
54. In the photo–electric effect which determines the
number of ejected
electrons ? (a) the brightness of the incident light (b) the frequency of the
incident light (c) nota
|
|
55. What convinced Rutherford
that the gold foil was mostly empty space? (a) finding most alpha particles were
un-deflected (b) finding some alpha particles bounced backwards
|
|
56. What convinced Rutherford
that the particles of the gold foil in empty space were massive? (a) finding most alpha particles were
un-deflected (b) finding some alpha particles bounced backwards
|
|
57. If the electron in a hydrogen atom obeyed classical
mechanics instead of quantum mechanics, what kind of spectrum would it emit ?
(a) a continuous spectrum (b) a line spectrum
|
|
58. In terms of wavelength de Broglie said that the smallest orbit that an electron can have
about the hydrogen nucleus is (a) one wavelength
(b) two wavelengths (c) three wavelengths (d) one-half
a wavelength (e) nota
|
|
59. What is the maximum number of paths for
de-excitation available to a hydrogen atom excited to level 3 (n = 3) in
changing to the ground state (n = 1) ?
(a) one path (b) two paths (c) three paths (d) nota
|
|
60. What type of radiation---alpha, beta, or gamma---
produces the greatest change in atomic number? (a) alpha (b) beta (c) gamma
|
|
61. True or False. It is possible for a common hydrogen nucleus to emit an alpha
particle (a) True (b) False
|
|
62. X-rays are
most similar to which of the
following? (a) alpha rays
(b) beta rays (c) gamma rays
|
|
63. What do all
isotopes have in common? (a) same number
of protons
(b) same number of neutrons
|
|
64. Which force tends to hold particles in an atomic
nucleus together? (a) strong force (b)
electric force
|
|
65. Radiation from a point source obeys the inverse
square law.
If a Geiger counter 1 m from a small sample registers
360 counts per minute, what will be the count rate (in counts per
minute) 3m from the source ? (a) 180 (b) 90
(c) 40 (d) nota
|
|
66. When
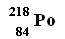 emits an alpha particle, it transforms to a different
element. What’s the atomic mass number
of the new element? (a) 213 (b) 214 emits an alpha particle, it transforms to a different
element. What’s the atomic mass number
of the new element? (a) 213 (b) 214
(c ) 215 (d) 222 (e) nota
|
|
67. In the previous problem what is the atomic number of the new
element? (a) 80 (b) 86 (c) 82
(d) nota
|
|
68. If a sample of radioactive isotopes has a half life
of 1 day, how much of the original sample is left at the end of the second day?
(a) one –half (b) one quarter (c) one-eighth
|
|
69. Most of today’s nuclear power plants use (a) fusion
(b) fission
|
|
70. In fission the combined mass of the fission products
is (a) less than the mass of the original uranium nucleus (b) more than the
mass of the original uranium nucleus
|
|
71. In a nuclear fusion reaction ,
which has more mass, the initial hydrogen isotopes or its products ? (a)
initial hydrogen isotopes
(b) products
|
|
72. Chain reactions in a fission reactor are caused by
(a) kinetic energy (b) energy conversion (c) mass conversion (d) ejected neutrons
|
|
73. A common nuclear power reactor (a) heats water (b) generates electricity
directly (c) gets energy from nothing
|
|
74. In both fission and fusion, energy is released
while mass (a) decreases (b) remains unchanged; is conserved (c) increases
(d) may increase or decrease
|
|
75. In either a fission or fusion event, a quantity
that remains unchanged is (a) kinetic energy (b) mass (c) number of nucleons
(d) binding of nucleons
|