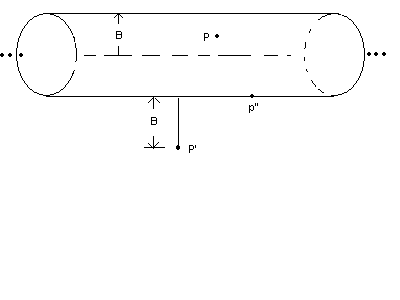
just above the surface of the conductor ? Derive E. Show all steps.
(d) (5 points)What is the direction of the electric field vector
P' ? Indicate by drawing an arrow at that point.
|
Test 3 from Tu, Thu Lecture, Aug 2001 |
1. (30 pts) FORCE AND FIELD FROM A LINE OF
CHARGE, CONDUCTORS;
QUIZ 2 #4;#20,#21,
#44, #45, #46.
Cylindrical Symmetry, model for a wire to CD player?
(c) (3 points) What is the magnitude E of the electric field at point P''
just above the surface of the conductor ? Derive E. Show all steps.
(d) (5 points)What is the direction of the electric field vector ![]() at point
at point
P' ? Indicate by drawing an arrow at that point.
(e) ( 2 points) What is the direction of the electric field vector ![]() at point
at point
P'' ? Indicate by drawing an arrow at that point.
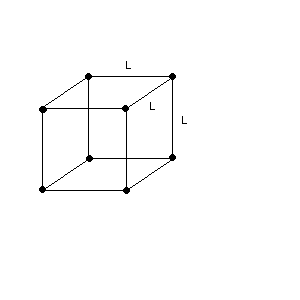
Model for a cubic ionic molecule in unstable equilibrium? Check it out.
4B SP12 REFERENCE: POTENTIAL
ENERGY OF A CUBIC SYSTEM OF POINT CHARGES :2. (36 points) A cube of side L has a point charge at each corner, each of the same charge q and same mass m.
(a) (2 points) What is the formula in terms of n for the number of terms in the expression for the potential energy for n charges ?
(b) (16 POINTS) What is the potential energy of the configuration below? Use symbols. You can answer this question by using the information of the solution to part (a) and/or by looking at the diagram below carefully.
(c) (18 POINTS) Suppose the charges are released from rest in the cube configuration shown. The charges then fly off to infinity. What is the speed v of each charge when they reach infinity ? Use symbols. Show all work !!!!
3. EXTRA CREDIT. 9 points.
A spherical capacitor has charge Q on the inner shell and charge -Q on the outer shell. The outer shell has radius b and the inner radius a. Check the diagram below. It might be a highly simplified model of a charged spherical gaseous layer surrounding a small planet. Here's some of the physics you should know about this scheme. Use symbols always:
(a) (2 points) Find the magnitude E of the electric field at a distance r from the central axis of the capacitor if b < r ?
(b) (2 points) What is the magnitude E of the electric field at a distance r from the center of the capacitor if a < r < b? Derive E. Show all steps.
(c) (2 points) Derive the capacitance of the system.
(d) (3 points) What is the rise in temperature if the energy in the capacitor is used to heat up a sample of water of mass M and specific heat Cw? Use symbols Q, a, b, and any other relevant constants.
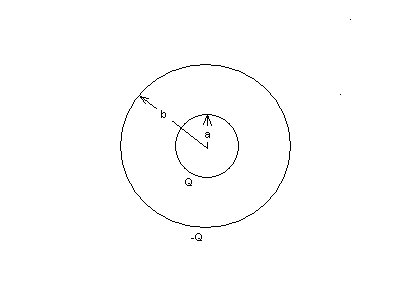
| Solution: (a) E = 0 since zero net charge is enclosed by any Gaussian surface larger than b in radius. (b) E = kQ/r2 Remember to derive this using spherical symmetry: E(4·pi·r2) = qenc/eo . So that E = Q/(4·pi·eo·r2) = kQ/r2 . Note qenc = Q, since the radius of the Gaussian surface is between a and b and only encloses Q on the inner sphere ! (c) See the derivation on page 808-9, example 26.3. (d) Q2/2C = M·Cw ·(Tf - Tf). Solve for (Tf - Tf) |