|
TEST 2 AU ‘12 |
|
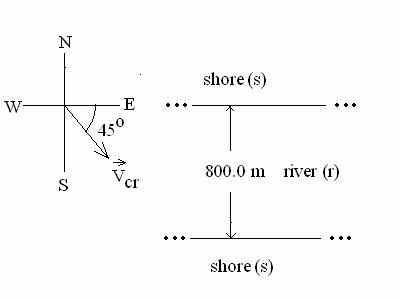
1. (36
POINTS) A canoe is on a river that is flowing due EAST with speed Vrs relative to the shore. River speed Vrs = 0.50
m/s. The
canoe has a velocity
(b) (16 points)
the direction of velocity
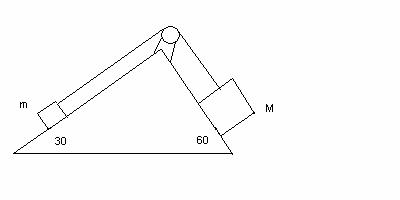
2. (36 POINTS)
(a) (16) What
is the magnitude of acceleration a of the blocks ? (b) (16 ) What is the tension T in the string ? (c) (4 ) Suppose the two
blocks start their motion from rest at t = 0. What is the common speed v ( in
m/s) of the blocks when t = 2.00
seconds
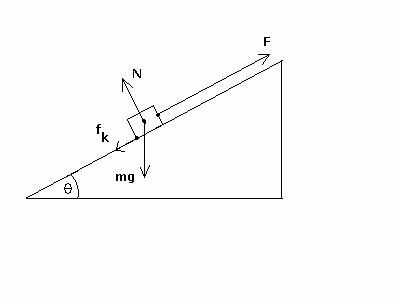
(a) (30 points) Assuming the positive x-direction is upward along the incline, what
is the acceleration ax along the incline?
4. (14 points) A place kicker kicks a
football from a point a horizontal distance
of 37.00 m from the goal. When kicked
(at t = 0), the ball leaves
the ground (at y = 0) with speed 21.00 m/s at an angle of exactly (a) (4 points) What is the vertical height h of the ball when it passes
over the goal? 5. (10 points) A 0.385-kg rock is swung in a vertical circular path
on a string that is 0.480 m long. Assume the speed v of
the rock is 3.90 m/s. Three points on
the circular path are shown: the top, the bottom and point Q at the end of a horizontal, radial line segment. Assume g = 9.80 m/s2.
What is, (a) (5 points) the magnitude aC of the
centripetal acceleration at point Q? (b) (5 points) the direction of the centripetal acceleration
at point Q? Draw an arrow whose tip points in the correct direction. (c) EXTRA CREDIT (3 points) What is the tension magnitude
T in the string at the bottom? (d) EXTRA
CREDIT (3 points) What is the tension magnitude T at the top? (e) EXTRA
CREDIT (3 points) What is the tension magnitude T at point Q where the rock is in a horizontal
position relative to the center. Short Answers. Multiple choice:
Mark your scantron with a #2 pencil. 2. The vertical component of the velocity of a
projectile remains constant during the entire trajectory of the projectile.
Neglect air resistance. (a) True (b)
False 3. A projectile is launched from ground level with a
certain speed. For any horizontal range less than the maximum
horizontal range, there are two possible launch angles that give the same
horizontal range. 4. A projectile is launched from ground level with a
certain speed. For the maximum horizontal range, the launch angle is (a) 90 degrees 5. The acceleration of a projectile remains constant
during the entire trajectory of the projectile. Neglect air resistance. (a) True (b) False 6. Mary needs to row her boat across a river that is
flowing East at What is the boat’s speed relative to the shore? (a) 7.0
m/s (b) 1.0 m/s 8. A satellite moves in a circular orbit at constant speed. The
satellite’s acceleration is zero. (a) True
(b) False 9. Force is a vector quantity. True or False. (a) True (b) False 13. Mass is a measure of how difficult it is to
change the velocity of an object. True or False. (a) True (b) False 14. In the
absence of a net force, a moving object will (a) stop immediately (b) slow down and eventually some to a
stop (c) move faster and faster (d) move with constant velocity 15. Neglect
air resistance. A ball is thrown upward. When it reaches its maximum height,
the net force on the object is zero.
True or False. 16. A ball is thrown upward in the air. Neglect air resistance.
When it is rising after being thrown
and reaches half of its maximum height, the net force magnitude acting on it
is (a) equal to its weight (b) less than its weight (c) zero 18. From
Newton’s Third Law, action-reaction forces are (a) equal in magnitude and point in the
same direction (b) equal in magnitude and point in opposite directions. (c) )
unequal in magnitude and point in opposite directions 19. The mass of the Moon is about 1/80 of the mass
of the Earth. Therefore the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on the
Moon is about 80 times the magnitude of the force exerted by the Moon on
Earth. True or False. (a) True (b)
False |