|
1. (40 points) A car is traveling in the positive x-direction with a constant speed of
30.0 m/s. The car passes a motorcycle cop at t = 0 and x = 0. At that same instant in time (t = 0), the motorcycle accelerates from rest with acceleration 3.20 m/s2 in the positive x-direction.
(a) (3 point) How far (in meters) has the motorcycle traveled
when it catches up with the car?
(b) (3 points)
What is the speed (in m/s) of the motorcycle when
it catches up with the car?
(c) (30 points) How
far (in
meters) has the motorcycle traveled when its
velocity is one-half the velocity of the car?
(d) (4 points) Sketch an x-t graph of the motion of both objects, car and
motorcycle, on the axes below. Label the axes , showing the value of
x and the time t when the cop catches up with the car.
(e) (4 points) Extra Credit-SEE QUIZ 4.
What is the
relative speed
between the motorcycle
and car when the cop catches up with the
car?

2. (40 POINTS)
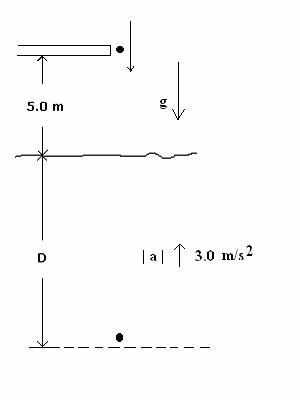
A wood
ball is thrown
with initial speed 2.0 m/s
downward
toward a lake from a diving board that is 5.0 m above the water. After entering the water, the wood ball slows down
and sinks toward the bottom
of the lake. See diagram below. Note that the scales shown may not be accurate
and thus could be different from your computations.
The lake
is very deep so the wood ball never reaches the bottom. In the water, the magnitude of the upward directed
acceleration is |a| =
3.0 m/s2.
(a) (37 points) At what distance D below the surface does the ball travel
before momentarily coming to rest ?
(b) (3 points) What is the speed of the ball when it arrives at the
water surface again?
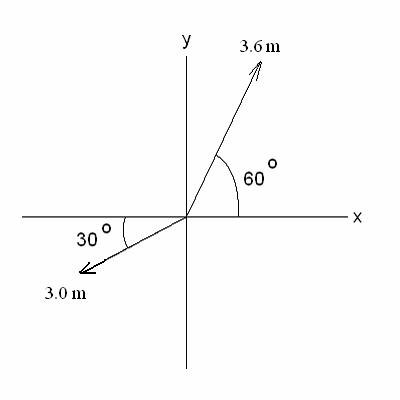
3. (a) (20) In the diagram
below, 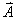 has magnitude 3.6 m
with the direction shown. has magnitude 3.6 m
with the direction shown. 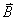 has
magnitude 3.0 m and points in the 3rd quadrant with direction
shown. Write each
vector component in the blanks provided. Show work in spaces below
and next pages. has
magnitude 3.0 m and points in the 3rd quadrant with direction
shown. Write each
vector component in the blanks provided. Show work in spaces below
and next pages.
(b) (11) Compute the magnitude 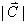 of the vector sum of the vector sum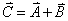 . Show work in spaces below
and next pages . . Show work in spaces below
and next pages .
(c) (9) Find
the
direction
of the vector sum 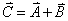 by doing the
following: by doing the
following:
(i)
Show the direction by drawing this vector
sum
in the correct quadrant on the blank
axes provided on next page.
(ii)
Calculate the related (reference) angle 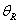 the vector makes with
the x-axis. Show this
angle in sketch, with work. the vector makes with
the x-axis. Show this
angle in sketch, with work.
Ax = __________________ Ay =
______________________
Bx
= _________________
By
= _______________________
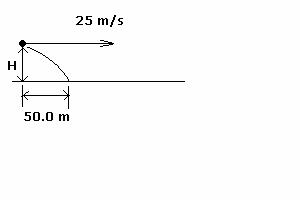
4. (10 points) A ball thrown
horizontally at 25 m/s
travels a horizontal
distance of 50.0 m before hitting the ground. From what height H
above the ground was the ball thrown?
Short Answers. Multiple choice: Mark your scantron with a #2 pencil.
1. It is possible to be moving and have zero
acceleration.
(a) True (b) False
2. An object moves in a straight line at constant
speed. The net force on
the object must (a)
not zero (b) zero (c)
infinite (d) none of the above
3. When the velocity of an object is zero, the object is
(a) moving (b) at rest
4. When the velocity and
acceleration point in opposite
directions, the speed of the object
(a) increases (b) decreases (c) is constant
5. Assume no air resistance. An object is released
from rest above the ground. As the object
moves down, the acceleration magnitude is
(a) 0 (b) 9.8 m/s2
6. Assume no air resistance. An object is thrown downward from above the ground. As the object moves down, the
acceleration magnitude is
(a) 0 (b) more than 9.8 m/s2 (c)
9.8 m/s2
7. Assume
no air resistance. An object is thrown upward from
above the ground. As the
object rises, its acceleration magnitude
(a) decreases (b) increases (c) is constant
8. The slope of a line connecting two points on a position (x)
versus time (t) graph gives (a) the average
velocity (b) the instantaneous velocity.
9. The slope of a tangent line at a given time on a position (x)
versus time (t) graph gives (a) the average
velocity (b) the instantaneous velocity.
10. Assume no air resistance. A stone is thrown up. As the stone rises, its speed (a) increases (b) decreases.
11. Assume no air resistance. A stone is thrown up.
What is its speed at the highest point? (a)
the same as the initial speed
(b) 0
12. When the velocity of an object is zero, the object’s acceleration must be
zero. (a) True (b) False
|




