|
SAMPLE TEST 2 FROM AU ‘11 |
|
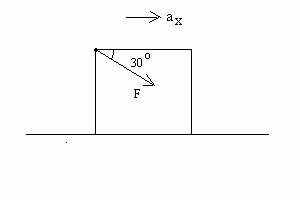
2. (53 POINTS) A person pushes a crate rightward along a rough horizontal surface by pushing
downward at 30 degrees below the
horizontal with a force of magnitude F = 50.0 (N). The crate has mass m = 10.0
kg. See the diagram below. Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the bottom of the crate and the surface is µk = 0.10. (b) (32 points) What is the horizontal acceleration ax
of the crate?
(a) (10 points) What is the magnitude N of the
normal force on the block of mass m? 4. Extra Credit (9 points) (a) (2 points) what is the direction of the block’s
centripetal acceleration?
|
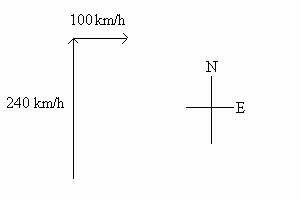
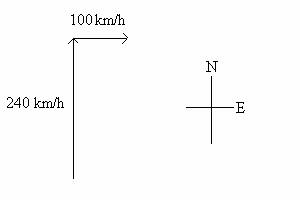
1. (52 POINTS) A pilot takes off from a city in
(a) (21 points) What is the magnitude of the airplane’s
velocity relative to the Earth?
(b) (21 points) What is the direction of the
airplane’s velocity relative to the Earth? Find this direction by computing the angle
this velocity makes with the North direction shown in the schematic of the
problem below.
(c) (10 points) The airplane lands at a small
airport directly East of
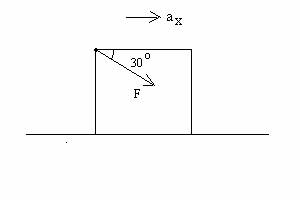
2. (53 POINTS) A
person pushes a crate rightward along a rough horizontal surface by pushing
downward at 30 degrees below the
horizontal with a force of magnitude F = 50.0 (N). The crate has mass m = 10.0
kg. See the diagram below. Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the bottom of the crate and the surface is µk = 0.10.
(a) (21 points) What is the magnitude N of the normal force acting on the
crate?
(b) (32 points) What is the horizontal acceleration ax
of the crate?
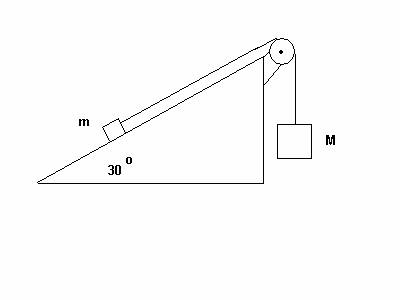
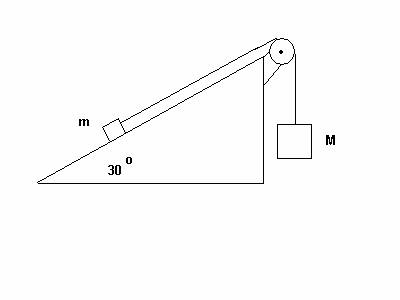
3.
(53 POINTS) Two blocks are connected by a light but sturdy string wrapped around a mass-less
pulley. The rough inclined surface
makes an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. The block on the inclined
surface has mass m = 5.0 kg. Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction between the
block of mass m and the inclined
plane is µk = 0.10. The
vertically hanging block has mass M = 50.0 kg. Assume the blocks begin their
motion from rest.
(a) (10 points) What is the
magnitude N of the normal force on the block of mass m?
(b) (5 points) What
direction does the hanging block move, up or down? Circle one.
(c) (18 points) What is the common magnitude a of the acceleration of the
blocks?
(d) (14 points) What is the magnitude T of the tension in the string?
(e) (6 points) What is the speed of the hanging mass after it has
moved a vertical distance of 1.50 m (assuming the hanging mass has not yet hit
the ground and the block of mass m has not yet reached the upper edge of the
incline)?
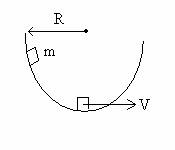
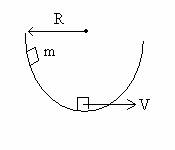
4. Extra Credit (9 points)
A 7.00-kg block slides along a smooth
hemispherical bowl of radius R = 1.0 m. The block starts from rest below the
upper left edge of the bowl and slides toward the bottom. At the bottom the
speed of the block is 4.00 m/s. At the bottom,
(a) (2 points) what is the direction of the block’s
centripetal acceleration?
(b) (2 points) what is the
magnitude the block’s centripetal acceleration?
(c) (5 points) what is the magnitude N of the normal force on
the block?