|
1.
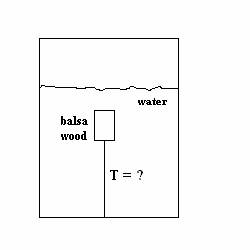
(40 POINTS) In a Chabot College physics lab
experiment, a piece of balsa wood is completely submerged under the water.
The wood is at rest and is tethered by a string to the bottom of a container
of water. The balsa wood has volume is
1.34x10 -6 m3 and density of 0.16 x10 3
kg/m3. Water, on the other
hand, has density 1.00x103 kg/m3. Answer the following questions and show all
work and reasoning.
(a) (6 points) What is the direction of the buoyant
force acting on the wood, up or down ? Circle “up”
or “down.”
(b) (6 points) What is the direction of the tension
force acting on the wood, up or down ?
Circle “up” or “down.” ?
(c) (6 points) What
is the direction of the force of gravity acting on the wood, up or down ? Circle “up”
or “down.”
?
(d) (22 points) What is the magnitude
T of the tension in the string?
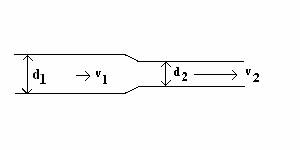
2. (18 POINTS) You
are a medical professional attempting to explore the problem of blood
pressure drops in diseased, narrowed
arteries. The arteries have
approximately circular cross-section.
In a section
of an artery, the diameter d1 is 0.0050 m and the speed v1
of the blood is 0.500 m/s. The
section narrows into another segment of artery with diameter d2 = 0.0022 m . The
height relative to the laboratory floor does not change (y1 = y2)
. The density of blood is 1.06x103 kg/m3. NOTE: The diagram below shows dimensions and arrows
qualitatively and may not be exactly
at scale.
(a) (2 points) What
is the circular cross-sectional area A1
of the first section of artery?
(b) (2 points) What is the circular cross-sectional
area A2 of the second section ?
(c) (5 points) What is the speed v2 in the narrow section of artery?
(d) (7 points) What is the pressure difference P1
– P2 between the two sections?
(e) (2 points) Short
answer in sentence form or math form; just clearly explain your work: It was
mentioned in class a
drop in pressure could lead to the collapse of the narrow section of artery.
Explain. What would be one major consequence of such a collapse?
3. (30 points) When a container
is filled to the brim with liquid, what happens when the temperature rises? You
are doing a controlled experiment on a strange, liquid metallic substance.
A glass flask has volume
1.0x10 -3 m3 at 0.0 0C and is completely filled (to the brim) with
a strange, liquid metal at this temperature. The volume thermal
expansion coefficient of glass is βg
= 1.7x10 -5 (oC) -1. When the flask and metal are warmed
to 57.0 oC , some of the liquid metal overflows and the metal’s
volume thermal expansion
coefficient is found to be βm
= 18x10 -5 (oC)-1.
What is the volume of fluid metal that overflows ? When done, you might want to convert your
answer to cm3 to better
see the spill.
4 . (30
points) Calculating required
heats. You have a large supply super-cooled ice at -10.0
oC to do informal experiments in
your college dorm room. Thus, the
initial temperature for all parts of
the problem below is -10.0 oC .
You will also need the following information: Specific heat of ice Ci
= 0.480 cal/(g·oC );
heat of fusion of water Lf = 79.9
cal/g, and specific heat of water Cw
= 1.00 cal/(g·oC ).
(a) (20 points) How
much heat is required to convert 12.0 g of
ice at
-10.0 oC to pure water at 55.0 oC?
(b) (10 points) How much heat is required to convert 12.0 g
of ice
at
-10.0 oC to a mixture of water and ice 0oC
assuming the mixture is 50 % water? In
other words, half
the 12 g piece of ice is melted.
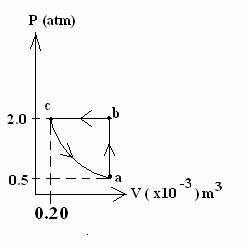
5. (40 POINTS) Below is a PV diagram showing a cyclic
process for
0.0040 moles of an ideal monatomic
gas. The direction of the cycle is shown by the arrows on the curve. The
temperature does NOT change along segment ca – the process is isothermal from point c to point a.
The other 2 sections of curve are graphically vertical and horizontal
.
(a) (14 points)
What volume does the gas occupy at point a?
(b) (14 points)
What is the temperature at points a, b
and c?
For
parts (c), (d) and (e) below, indicate whether the heat Q has gone into or
out of the gas by referring to the sign, positive or negative, of your
answer.
(c) (2 points) How much heat went into or out of the
gas during segment ab?
(d) (2 points) How much heat went into or out of the
gas during segment bc?
(e) (2 points) How much heat went into or out of the
gas during segment ca?
For parts (f) ,
(g) and (h) below, indicate whether the change in internal energy ΔE int is
positive or negative by referring to the sign of your answer.
(f) (2 points) Find the change in internal energy
during segment ab.
(g) (2 points) Find the change in internal energy
during segment bc.
(h) (2 points) Find the change in
internal energy during segment ca.
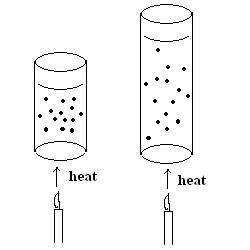
6. (30 POINTS) An ideal gas undergoes a reversible
expansion at
25.0 oC. During the expansion, the gas does 1825 J
of work moving the piston upward as indicated in schematic below.
(a) (24 points) What
is the change in entropy ΔS of the gas?
(b) (6 points)
Suppose the volume of the gas is doubled during the expansion. What is
the number of moles n of the gas?
7. EXTRA
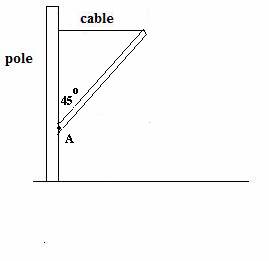
CREDIT (14 points) A uniform horizontal beam has a mass of 13.0 kg . As you
see below, the beam makes an angle of 45 degrees with a vertical pole. The beam’s right end is connected to a horizontal, light (essentially mass-less ) cable. The beam’s left end is hinged at pivot A on
the rigid, fixed pole. The left end of the cable is also attached
to the pole. See figure. Show
all work.
(a)
(6 points) What is the tension
T in the cable?
(b) (2 points)
What is the horizontal component
of force FH exerted
by pivot A on the beam?
(c) (2 points) What is the vertical component
of force Fv exerted by pivot A on the beam ?
(d) (4 points) Assuming the beam length is 1.0 m, suppose a vandal
severs the cable such that the tension becomes zero. Consider the moment just after the cable is cut and the
beam is in a horizontal position. At
that instant, what is the magnitude of the torque (about pivot A) exerted by the
gravitational force? What is the
magnitude of the beam’s
angular acceleration
about point A at this instant?
|




