|
Final 2B SP ‘12 |
|
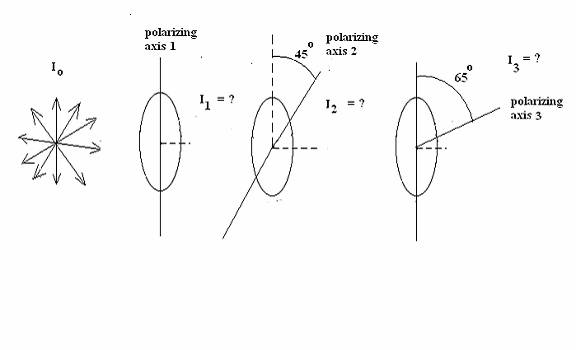
1. (30 POINTS)
(c) (10
points) What
is the Intensity of the light after it passes through Sheet 3? SOLUTIONS answers in W/m*m. (a) I1 = Io/2
= 20.5 (b) I2 =
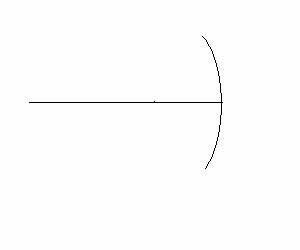
I1*cos245 = 10.25 (c) I3 = I2*cos220 = 9.05 2. (30 POINTS) A concave
mirror has a radius of curvature R = 10.0 cm. When an upright object is placed a
distance do in front (on the left)
of the mirror, a real, inverted image is produced on the same side (on the left) with magnification m = -2.
SOLUTIONS answers in cm (a) f = R/2 = 5.00 (b) 1/f = 1/do
+ 1/di and di = 2*do leads
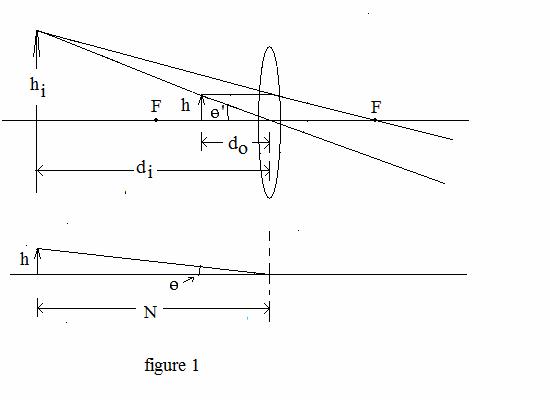
to do = 7.5 (c) di = 15 3. (36 points) MAGNIFYING GLASS: A magnifying glass
is formed from a single double convex (converging) lens with a focal length
of f = +12.0 cm . The lens, with focal
points labeled by F, is shown in the schematic (figure 1) next page. It could be the model for a Bart passenger’s reading
glasses while she scans the afternoon’s news headlines. The distance | di
| is the distance between one of
the lens’s and the virtual IMAGE of the news story
of the Sharks victory she wants to read about. Note:
do SOLUTIONS answers in cm or no units (a) 1/f = 1/do
+ 1/di and di = -60 (b) M = 25/f =
2.08 (d) M = (2.08)*(0.01)
= 0.0208 4. (36 points) TWO SLIT INTERFERENCE: A coherent electromagnetic
wave of wavelength 520 nm passes
through two thin slits that are a
distance d = 0.0400 mm apart. The light then falls on
a screen a distance R = 70.0 cm away. (e) (4
points) In this problem, in what range is the electromagnetic (i) x-ray range (ii) visible range (iii) ultra–violet range (iv) in the range
of radio waves SOLUTIONS answers in cm (a) y3 =
3*lambda*R/d = 2.73 cm (b) y3 = 2.5*lambda*R/d = 2.28 cm; difference =
0.455 cm (d) 2*0.455 cm = 0.91 cm (e) ii visible
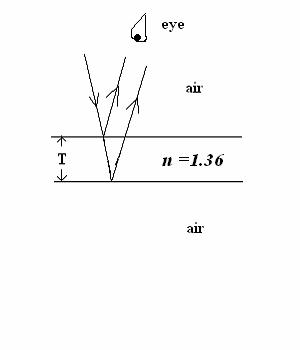
SOLUTIONS answers in nm and cm (a) T =
lambda/(2*n) = 172.8 nm (b) T =
lambda/(4*n) = 86.4 cm 6. (26 points) SINGLE
SLIT DIFFRACTION: A coherent electromagnetic wave of wavelength 656.3 nm passes through a single slit with width a = 0.460 mm. Assume the screen is 1.82
m from the slit. (i) x-ray range (ii) visible range (iii) ultra–violet range (iv) in the range
of radio waves SOLUTIONS answers mm (a) y1 = 1*lambda*R/a = 2.596 mm (b) y5 - y1 =
4*lambda*R/a = 10.3867 mm (d) ii visible 7. (30 points) Cosmic ray particles are created 57.00
km above the Earth’s surface (as measured in the Earth’s reference frame).
The average lifetime of a particle, measured in its own rest frame, is 2.00 x10 - 6 seconds. (b) (5 points) In the Earth’s frame, how far does the particle travel during its
lifetime? (c) (5 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part (b) to the particle’s original height in the
Earth’s frame? (d) (5 points) In the particle’s frame, how much
closer does the Earth get during the particle’s lifetime? (e) (5 points) In the particle’s frame, what is its initial height above the Earth’s surface? (f) (5 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part (d) to the particle’s initial height in the particle’s frame given in part ( e) ? SOLUTIONS answers use sqrt(1 – v2/c2) = sqrt(1 – 0.98202) =alpha = (d) d’ = =
0.9820*c*2.00x10-6 s = 589.2
m (e) 57*alpha
= 10.7665 km (f) d’/10.7665
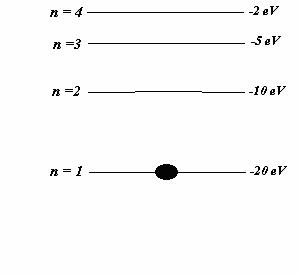
km = 0.0547 8. (10 POINTS) Below is a
energy level scheme of a hypothetical one-electron element Mathematicum. The potential energy is taken to be
zero for an electron at an infinite distance from the nucleus. (a) (2 points) How much energy does it take to ionize an electron
from the ground state level (n = 1) ? (b) (6 points) What will be the final electron state
if a photon of energy of 10 eV strikes a Mathematicum
atom initially in its ground state level (ni = 1)? In
other words, find the
value nf of the final state if the atom absorbs a 10-eV
photon. (d) EXTRA CREDIT: (12 points) Photons emitted in the
Mathemticum
transitions n
= 3 to n = 1 will eject photoelectrons from a certain metal. The work function of the metal is 4.00 eV
. The work function is the minimum photon energy needed in order for an
electron to escape the metal. Use conservation of energy to answer the following
question: What is the kinetic energy
of the ejected electrons? SOLUTIONS answers in eV.
(b) n = 2 (c) photon
not absorbed (d) KE = 15 eV – 4 eV = 11 eV. |