|
|
|
DOWNLOAD, PRINT OUT AND DO WORK ON SEPARATE SHEETS OF PAPER NEATLY. * DO NOT USE PAPER SHEETS TORN FROM A SPIRAL NOTEBOOK. * USE CLEAN WHITE PAPER, STAPLED TOGETHER, THE PROBLEMS ORDERED CHRONOLOGICALLY. WRITE ON ONE SIDE OF EACH SHEET ONLY. THANK YOU. |
|
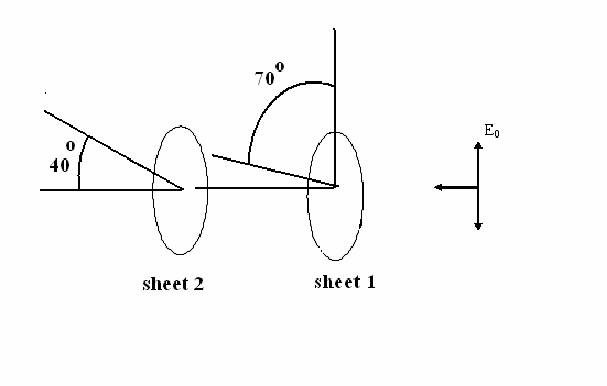
1. (22 POINTS)
(a) (10
points) What is the Intensity of the light after it passes through Sheet 1 before reaching Sheet 2. (c) ( 2 points) We assume the initial leftward moving electro-magnetic
wave (before reaching sheet 1) is linearly polarized in the vertical
direction with the electric field oscillating up and down parallel to the page. For the initial wave, suppose at
a given location in space and moment in time, the electric field points
vertically up.
What direction is
the magnetic field vector at that same location and instant of time, IN or OUT of the page.
Explain your reasoning or any right hand rules you use. |
|
2. (22 points) A converging lens has a focal length f = 25 cm.
When an upright object is
placed a distance do in front (on the left) of the lens,
a real, inverted image is
produced on the other side (on the right)
with magnification m =
-2. FOR |
|
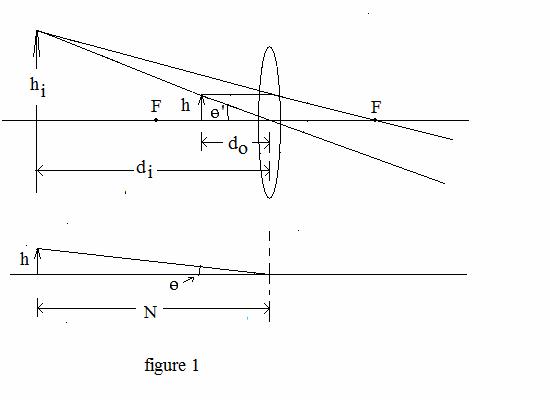
3. (22 points) A magnifying glass is formed from a
single double convex (converging) lens with a focal length of f = +12.0 cm
. The lens, with focal points labeled by F, is shown in the schematic (figure 1) below. It could be the model for a Bart passenger’s reading
glasses while she scans the afternoon’s news headlines. The distance | di
| is the distance between one of
the lens’s and the virtual IMAGE of the news story
of the Sharks victory she wants to read about. Figure 1 below applies to general situations and also to part (a) with certain adjustments. Figure 1
also shows the unaided eye viewing the object a distance 25 cm away. Note that N =
near point distance = 25 cm. |
|
|
|
4. (22 points) Coherent light of wavelength 525 nm
passes through two thin slits that are a distance d = 0.0415 mm apart. The light then falls on a screen a distance R
= 75.0 cm away. How far away from the central bright fringe on the screen is:
|
|
5. (22 points) Light of wavelength 656.3 nm passes through
a single slit with width a = 0.450 mm. Assume the screen is
R = 1.75 m from slit.
|
|
6. EXTRA CREDIT. (12 points) A muon is created 52.00
km above the Earth’s surface ( as measured in the
Earth’s reference frame). The average lifetime of a muon,
measured in its own rest frame, is
2.20 x10 - 6 seconds. (c) (2 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part (b) to the muon’s
original height in the Earth’s frame? (d) (2 points) In the muon’s
frame, how much closer does the Earth get during the muon’s
lifetime? (e) (2 points) In the muon’s
frame, what is its
initial height above the Earth’s surface? (f) (2 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part
(d) to the muon’s
initial height in the muon’s frame given
in part ( e) ?
|
6. EXTRA CREDIT. (12 points) A muon is created 52.00
km above the Earth’s surface ( as measured in the
Earth’s reference frame). The average lifetime of a muon,
measured in its own rest frame, is
2.20 x10 - 6 seconds.,
In the frame of the muon, the Earth is moving toward
the muon with speed 0.9860c. Thus, in the frame of
the Earth, the muon is moving toward the Earth with
speed 0.9860c.
(a) (2 points) In
the Earth’s frame, what is the lifetime of the muon?
(b) (2 points) In the Earth’s frame, how far does the muon travel during its lifetime?
(c) (2 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part (b) to the muon’s original
height in the Earth’s frame?
(d) (2 points) In the muon’s frame, how much closer does the Earth get during the
muon’s lifetime?
(e) (2 points) In the muon’s
frame, what is its
initial height above the Earth’s surface?
(f) (2 points) What is the ratio of your answer to part (d) to the muon’s
initial height in the muon’s frame given
in part ( e) ?
6.