|
TEST AU12 |
|
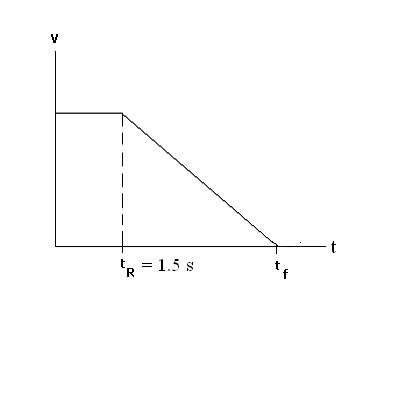
1.† ( 40 points) A car travels down a lonely road at constant
velocity 20.0† m/s. Suddenly,† at t = 0,†
the driver sees a deer in the road. After a† reaction time tR† = 1.5 seconds,† the driver steps on the brakes and the car
then decelerates (slows down)† at constant acceleration with magnitude 4.00 m/s2 before
coming to rest at time tf. Below is the
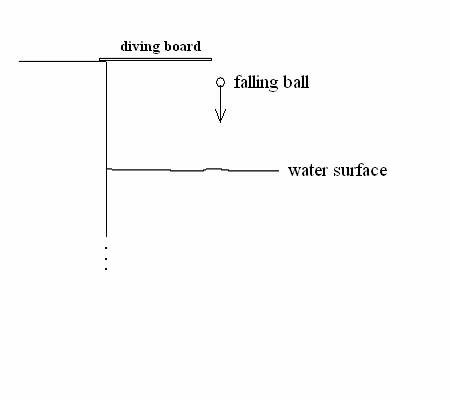
velocity v vs. time t graph of the carís motion. (c)† (5 †points)† What is the carís displacement †(in m) at t = 4.0 seconds? 2. (40 points) A ball is thrown downward †with initial speed 2.00 m/s toward a lake from a diving
board that is 11 m above the surface of the water. While the ball is in the
air, it is in free fall with
acceleration of magnitude g directed downward.† After the ball hits the water, it slows down and sinks downward with an upward
acceleration of †magnitude 3.00 m/s2
.†† (a) (20 points) What is the ballís speed just before it hits the water surface?
(b) (20 points) What is the maximum† depth D below the water surface †reached by the †decelerating†† ball?
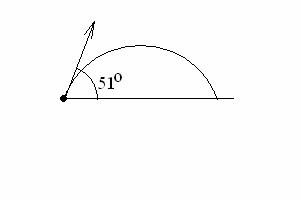
3.† ( 40
points) A place kicker kicks a football from a point a horizontal distance of 37.00 m from the goal.†† When kicked (at t = 0), the ball leaves† the ground (at
y = 0) with †speed 21.00 m/s at an
angle of (a) (24 points) What is the vertical† height h of the ball when it† passes†
the goal? † Ax† = __________________ Ay =
______________________
Short Answers. Multiple choice:
Mark your scantron with a #2 pencil.†† 1. It is possible to be moving and have zero
acceleration. 2. An object moves in a straight line at constant
speed. The net force on† the object
must† be (a) not zero† (b) zero†
(c)† infinite (d) none of the
above
5. Assume no air resistance. An object is released
from rest above the ground. As the object†
moves down, the acceleration magnitude is† 6. Assume no air resistance. An object is thrown downward from† above the ground.† As the object moves down, the acceleration
magnitude is 7.† Assume no
air resistance. An object is thrown upward† from†
above the ground.† As the object
rises, its acceleration magnitude† 8. The slope of a line connecting two points on a position† (x) versus
time (t) graph gives (a) the average†
velocity (b) the instantaneous velocity. 9. The slope of a tangent line at a given time on a† position (x)
versus time (t) graph gives (a) the average†
velocity (b) the instantaneous velocity. 11. Assume no air resistance. A stone is thrown up.
What is its speed at the highest point? (a)†
the same as the initial† speed††
(b) 0†† |